Ans:
If you want to increase re usability in inheritance then abstract classes are good. If you want implement or force some methods across classes must be for uniformity you can use a interface. So to increase re usability via inheritance use abstract class as it is nothing but a base class and to force methods use interfaces.
Abstract Class:
When we have the requirement of a class that contains some common properties or methods with some common properties whose implementation is different for different classes, in that situation, it's better to use Abstract Class then Interface.
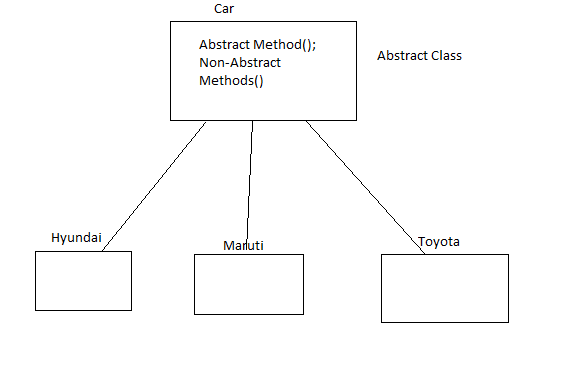
Example:
Important:
So, in those cases, we will use abstract class where we want to restrict the user from creating the object of parent class because by creating object of parent class, you can't call child class methods. So, the developer has to restrict accidental creation of parent class object by defining it as abstract class.
So, I think, in these ways, we can use abstract class in our real time project.
Here is my Hyundai class which is derived from Cars.
A new feature for the Hyundai car is Introduced called GPS which is not supported in Toyota cars. Then, how can we implement and which way we can implement these?
Here, we have certain options like
If you want to increase re usability in inheritance then abstract classes are good. If you want implement or force some methods across classes must be for uniformity you can use a interface. So to increase re usability via inheritance use abstract class as it is nothing but a base class and to force methods use interfaces.
Abstract Class:
When we have the requirement of a class that contains some common properties or methods with some common properties whose implementation is different for different classes, in that situation, it's better to use Abstract Class then Interface.

Example:
- using System;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public abstract class Cars
- {
- //put all the common functions but diffrent implementation in abstract method.
- public abstract double price();
- public abstract int getTotalSeat();
- public abstract string colors();
- //put all the common property in normal class
- public string Wheel()
- {
- return "4 wheeler";
- }
- public string CheckAC()
- {
- return "AC is available";
- }
- public string CallFacility()
- {
- return "Call Facility supported";
- }
- }
- }
Important:
So, in those cases, we will use abstract class where we want to restrict the user from creating the object of parent class because by creating object of parent class, you can't call child class methods. So, the developer has to restrict accidental creation of parent class object by defining it as abstract class.
So, I think, in these ways, we can use abstract class in our real time project.
Interface:
Now, I will narrate a real time scenario where we can use interface. I will go for the same example that I have done earlier.
Now, here is my Toyota class which is derived from Cars.
- using System;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Cars
- {
- public string Wheel()
- {
- return "4 wheeler";
- }
- public string CheckAC()
- {
- return "AC is available";
- }
- public string CallFacility()
- {
- return "Call Facility supported";
- }
- }
- }
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Toyota : Cars
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Toyota Toy = new Toyota();
- Console.WriteLine(Toy.CallFacility());
- Console.WriteLine(Toy.Wheel());
- Console.WriteLine(Toy.CheckAC());
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
- using oops1;
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Hyundai:Cars
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Hyundai dust = new Hyundai();
- Console.WriteLine(dust.CallFacility());
- Console.WriteLine(dust.Wheel());
- Console.WriteLine(dust.CheckAC());
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
Here, we have certain options like
- Go for a new class defining the GPS method and inherit it to the Hyundai Class.
- Go for an abstract class and define GPS method and inherit it on Hyundai class and implement the GPS method there.
- Directly create a method in Hyundai class and consume it.
- Go for Interface
.
CASE 1 - By Using simple class
Let's find what will happen if we use a class there, and declare a method as GPS and try to inherit in Hyundai class.
Created a new class as "NewFeatures, as shown below. - Now, inherit the Hyundai class from NewFeatures. So, if we check this class, it was previously inherited from Cars class and for now, again inherits from NefFeatures class. So, it gives the following error when you try to run the program.
- class NewFeatures
- {
- public void GPS()
- {
- Console.WriteLine("GPS supported");
- }
- }
Now, run the program and find out the error.- using oops1;
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Hyundai:Cars,NewFeatures
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Hyundai hun = new Hyundai();
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CallFacility());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.Wheel());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CheckAC());
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
This is simple because C# does not support multiple inheritance. - CASE 2 - By using Abstract class
Now, go for abstract class and see what happens.Now, let's try to inherit from abstract class.- public abstract class NewFeatures
- {
- abstract public void GPS();
- }
So, here is the error I got.- using oops1;
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Hyundai:Cars,NewFeatures
- {
- public override void GPS()
- {
- Console.WriteLine("GPS supported.");
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Hyundai hun = new Hyundai();
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CallFacility());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.Wheel());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CheckAC());
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
- CASE 3 - Direct creating a method called GPS() inside Hyundai class
This is very relevant way to use a unique method but it has a small problem. If for any reason we forget to create such common method, then it will not ask to write methods.Today, we are using one unique method so that is OK we can remember and write the method. Suppose, we have hundreds of such common methods and we forget to write 2 of them then it will run but not give the expected output,so we have to skip the way and go for the fourth one by defining interface. - CASE 4 - By defining Interface
This is the most important case and we will see how it will solve our problem.Lets define the method in an InterfaceNow inherit the Interface from Cars and see without implementing the GPS() method.- interface INewFeatures
- {
- void GPS();
- }
As we have not implemented the method it will show the following error as follow.- using oops1;
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Hyundai:Cars, INewFeatures
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Hyundai hun = new Hyundai();
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CallFacility());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.Wheel());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CheckAC());
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
So, the problems which happen in case 3 can be easily solved by using Interface. Now, let's implement the method and see will it solve the problem which arises in Case1 and case2 as follows.
- using oops1;
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace oops1
- {
- public class Hyundai:Cars,INewFeatures
- {
- public void GPS()
- {
- Console.WriteLine("GPS supported.");
- }
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- Hyundai hun = new Hyundai();
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CallFacility());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.Wheel());
- Console.WriteLine(hun.CheckAC());
- hun.GPS();
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- }
- }
Thus, it resolves the demerits of all the above 3 cases. So, in this situation, we have to use Interface. Here, I have shown you the sketch diagram.


 So, the problems which happen in case 3 can be easily solved by using Interface. Now, let's implement the method and see will it solve the problem which arises in Case1 and case2 as follows.
So, the problems which happen in case 3 can be easily solved by using Interface. Now, let's implement the method and see will it solve the problem which arises in Case1 and case2 as follows.
